In the world of software development, interoperability is the ability of different devices, systems, and applications to work together in a coordinated manner, much like musicians in the Vienna Symphony Orchestra, regardless of their origin or technology. This concept is essential in digital transformation, where systems, such as a robotic application, must integrate with multiple platforms, including robotic control systems, artificial intelligence solutions, and industrial IT management platforms like ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or MES (Manufacturing Execution System).
The primary goal is to facilitate real-time data exchange for smarter decision-making. Interoperability plays a crucial role in robotics by enabling seamless integration between heterogeneous industrial production systems and digital platforms.
Benefits of interoperability
Adopting interoperability technologies in robotic application development brings multiple advantages, including:
- Intelligent asset management and remote monitoring of robots and machine tools, allowing centralized, real-time control of distributed systems.
- Optimized decision-making: With real-time data availability, organizations can enhance their responsiveness to unexpected events and optimize workflows.
- Scalability and modularity: Enabling the integration of new technologies, sensors, and robots without the need for complete system redesigns, supporting adaptability to future industrial needs.
- Cost and downtime reduction in production lines through the integration of heterogeneous systems, minimizing setup times and allowing quick reconfiguration and process flexibility in dynamic environments.
- Predictive maintenance and resource optimization: Using AI-based models to anticipate failures, optimize spare part usage, and extend equipment lifespan without compromising productivity.
FIWARE as an interoperability enabler
For robotic systems to integrate efficiently, they must be compatible with standardized platforms that enable intelligent data management and communication. FIWARE, which we work with in the ARISE project, is a set of technologies, architectures, and standards that accelerate the development and deployment of open-source solutions. As a leading technology in the European Union, FIWARE primarily contributes to the creation of interoperable tools and services for real-time data management and analysis, ensuring persistence, flexibility, and scalability, thereby enabling the development of customized applications without excessive costs.
Another key value proposition is its multi-sector nature. FIWARE’s standardized reference components and architectures allow any solution designed for a specific sector—such as manufacturing, logistics, or services—to be inherently interoperable with other verticals, including energy management, mobility, or emerging data spaces.
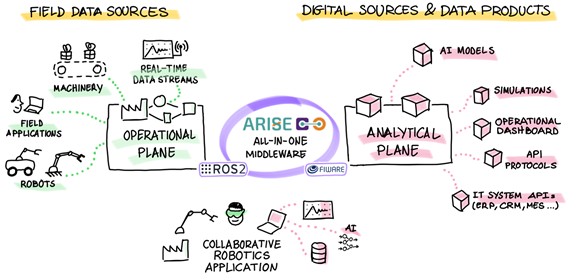
In ARISE, we develop robotic applications for human-robot interaction by integrating our ARISE middleware (a middleware solution that incorporates Vulcanexus, ROS2, FIWARE, and ROS4HRI) into four experimental environments. These environments explore connected robotic solutions with FIWARE in an Industry 5.0 scenario. One of these environments is in CARTIF, a laboratory for testing and validating technology in controlled environments (TRL 4-5). Figure 1 below shows this experimental setup:
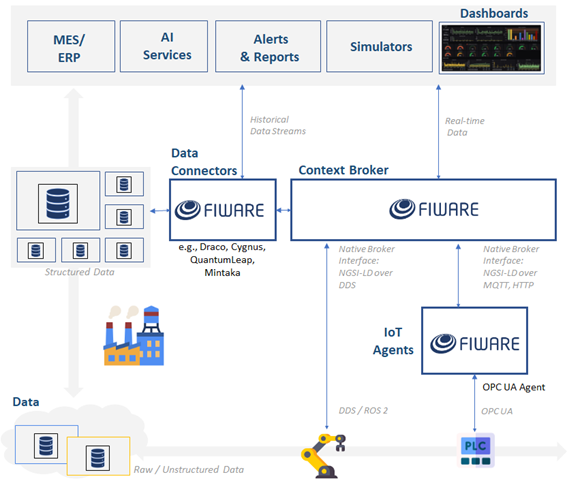
FIWARE plays a fundamental role in providing tools that enable interoperability between heterogeneous systems, ensuring seamless integration of real-time data and IoT devices, as well as dynamic data management from the operational level, allowing communication between different systems, devices, and platforms toward the analytical level. This ensures deep integration with enterprise IT/OT infrastructures (see Figure 2):
Designing a FIWARE architecture and key components
The design of a FIWARE architecture follows a modular approach, where components are integrated according to application needs. The architecture is built around its core component, the Context Broker, which manages real-time data flows. To implement FIWARE effectively, it is recommended to follow these steps:
- Define the use case: identify the application’s objectives and requirements.
- Select the appropriate architecture: include the Context Broker, IoT Agents, and other components as needed, converting heterogeneous protocols into FIWARE-compatible data. For example, the OPC-UA IoT Agent enables real-time management of data collected in industrial environments, facilitating interoperability with other systems.
- Integrate devices and systems: connect sensors, robots, or other systems via OPC-UA, MQTT, or other protocols.
- Implement security and access control: use Keyrock and PEP Proxy to ensure data protection, authentication, and access control.
- Store and analyze data: utilize Cygnus, Draco, or QuantumLeap for valuable insights, historical data storage, persistence, and Big Data analysis.
- Deploy in the cloud or local environments: consider FIWARE Lab or private infrastructure for hosting services.
- Monitoring and optimization: evaluate system performance and improve integration with platforms like AI-on-Demand or Digital Robotics. Wirecloud enables the creation of custom visual dashboards, facilitating easy integration with applications like Grafana and Apache Superset.
FIWARE component catalog: https://www.fiware.org/catalogue/
At CARTIF, we continue to invest in these technologies to build a future where system and platform collaboration is the key to success. Recently, we joined the FIWARE iHubs network under the name CARTIFactory. As an official iHub, it will not only promote FIWARE adoption but also serve as a reference center with its experimentation lab, fostering interoperability in robotic applications within our community and industrial ecosystem.
Interoperability is not just a technical requirement but a fundamental pillar for the success of digital transformation in industry. Technologies like FIWARE enable the connection of systems, process optimization, and the development of a flexible and scalable ecosystem. Thanks to this capability, companies can integrate artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced automation seamlessly.
Co-authors
Aníbal Reñones. Head of the Industry 4.0 Area, Industrial and Digital Systems Division
Francisco Meléndez. Robotics Expert and FIWARE Evangelist, Technical Coordinator of the ARISE Project (FIWARE Foundation)
